
|
Published: 24 March 2014
Flexible electronics to boot up new solar manufacturing industry?
Australia’s manufacturing industry could be given a welcome boost if it takes advantage of some of the latest research here and overseas to create ultra thin and flexible electronic devices, including solar cell films that could be integrated with windows and roofs.

|
|
This OLED light fitting can change its shape – just one of the amazing things you can do with flexible electronics. Credit:
Andy Zhou
|
Just last week, the University of Washington announced the thinnest ever light emitting diodes (LEDs), based on 2D semiconductors that are only three atoms thick – that’s 10,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair.
This research, as well as our own work on flat, atom-thin semiconductors, is helping to realise incredibly thin electronic devices that can bend, flex and even wrap around your arm.
This continually evolving field of flexible electronics promises to deliver products that are shaped, formed and coloured in ways that bear little resemblance to today’s rigid devices. Think roll-up TV screens, wearable devices and paper-thin solar cells as part of our everyday lives.
Given the exciting possibilities, we can expect intense consumer demand for flexible electronics products. The market will be big and pervasive, estimated to grow from A$16 billion last year to A$77 billion in 2023.
This huge market represents a major manufacturing opportunity for Australia. It’s now up to us as a country to step up and play our part.
What are flexible electronics?
Flexible electronics are just that: flexible. It’s this feature that has the potential to change the way we do things.
Two of the most promising areas for flexible electronics are thin film solar cells and revolutionary new displays known as organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs).
OLEDs are already found in mobile phones and even in curved televisions. They are now moving into lighting, allowing us to take advantage of large panels that emit uniform light, rather than point sources such as bulbs.
In Australia, the combination of R&D and design is already shining a light on the incredible possibilities OLEDs offer. Andy Zhou, a design graduate from Monash University, worked with CSIRO scientists to develop the Plus Pendant, a flat flexible light that showcases the potential of this technology.
Plus Pendant – an OLED luminaire.
Credit: Andy Zhou/CSIRO
Just as OLEDs can convert electricity into light, similar devices can convert light into electricity: organic solar cells.
What’s most exciting about this technology is that the absorbing materials (and even the electrodes that go on top of them) can be embedded on surfaces using conventional techniques such as screen printing. Just as 3D printing is set to change the way we manufacture many objects, printing of solar cells on demand is fast becoming a reality.
What role can Australia play?
Australia has a number of highly respected research groups working on thin film solar. Many of these groups are closely linked to research on traditional, silicon-based solar cells and rely heavily on chemistry.
The consortium of researchers that I am a part of recently installed a new printer that allows us to print solar cells the size of an A3 sheet of paper – the largest in Australia.
Printing Australia’s largest solar cells.
Credit: CSIRO
We’re working towards using these solar cells in products such as small advertising displays and portable lighting. We’re also developing materials and processes that will allow us to integrate them directly into building materials such as windows or steel roofing.
Further down the track, new advances such as perovskite-based solar cells are raising the possibility that printed solar could compete with more traditional cells on efficiency and cost.
Kick-start an industry
For Australia, printed solar cells are just one product that could kick-start a local flexible electronics industry.
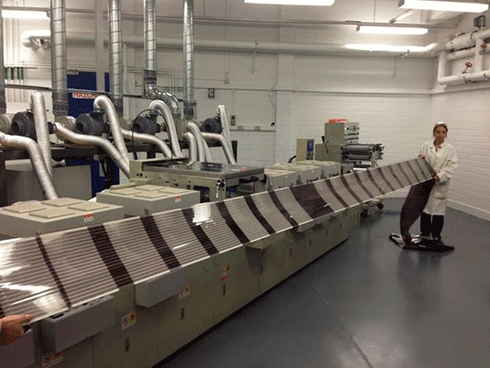
|
|
Printing solar cells by the roll. Credit:
CSIRO
|
We’re developing partnerships with many different companies to bring together end-users, component manufacturers and designers to create a flexible electronics ecosystem.
The companies positioned to take advantage of this opportunity will be involved in printing, coating, plastic forming and electronic integration as well as roofing, window and tile manufacturers.
There are even some auto suppliers that have begun to investigate how they might use flexible electronics for internal lighting. It is these businesses that diversify into new game-changing areas that will be best placed to tackle the challenges Australia’s manufacturing industry is currently facing.
Looking overseas, successful business models for flexible electronics in Europe, Germany, the UK and the US rely on clusters of small to medium enterprises (SMEs), each contributing a specific component to the final product. Australia’s rich SME sector is perfectly suited to this approach.
The danger for Australia is that if we wait until these technologies are truly ‘off-the-shelf’ then it is highly likely that the ‘shelf’ will be located overseas.
So the next step for Australia is for companies, industry groups and government to get together and talk about how to develop this capability for flexible electronics and foster a local skilled workforce.
We have the opportunity to take ownership of this for our manufacturing future. Let’s get on a roll.
Dr Scott Watkins leads CSIRO's research stream on Organic Photovoltaics (OPVs). CSIRO is a member of the Victorian Organic Solar Cell Consortium, which includes researchers from the University of Melbourne, Monash University, and industry partners BlueScope Steel, Innovia Films, Securency and Robert Bosch SEA. The aim of the consortium is to replace high-cost silicon based solar cells with low-cost, environmentally friendly, printable, thin-film, plastic solar cells. This article was originally published on The Conversation.



